Vascular diseases are a very common phenomenon that can happen to everyone. Like many other diseases, varicose veins have their own stages and, if the initial manifestations of pathology are most often accompanied by discomfort, the last stage is dangerous not only for health but also for human life. To avoid the beginning of consequences as serious, such as disability and others, it is necessary to know the main characteristics of the manifestation of varicose veins, its development and ways to prevent its complications.
The concept of varicose veins
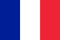
Varicose veins are a disease that affects the muscular layer and connective tissue of the vascular wall as well as your valve device. As a result, the veins are expanded, blood circulation in this place, reverse blood of the blood through the vessels.
Most people know the varicose veins at their feet. But there are other locations of the disease, as vessels can be affected anywhere on the body.
Most of the time, in medical practice, the varicose veins of the pelvic organs (bladder, uterus), perineum (scrotum, rectum, vagina) are diagnosed. However, in any case, the clinical image of the disease depends on the place of damage and the stage of the pathology.
Veins veins in men and their resources
At an early age (on average, 10 to 12 years old), a young man can find a disease as varicose veins of the veins of the scrotum. In the scientific, this state is called "varicocele".It can be found during a simple examination and palpation of the scrotum. Varicocele clinically is manifested by various symptoms, including:
- Pain on the side or half of the affected scrotum, intensifying after physical activity;
- gravity in the testis;
- infertility.
However, Varicocele often may not show and be identified by accident during a planned exam.
This disease distinguishes three stages:
- Light vein expansion, which can be seen when the patient performs the Valsalva sample (deformation);
- The veins are visible and palpated in a calm state of the patient;
- The vessels are quite altered, convincing, full of blood. The testis in the area affected by the disease is reduced in size, has a test consistency.
In adult patients, scrotum varicose veins are often diagnosed when treating a doctor with complaints from the inability to have a child. There is a theory that varicocele affects fertility (the ability to reproduce children) increasing temperature within the scrotum, which adversely affects the testis and spermatogenesis. In addition, this type of varicose veins in men is often combined with damage to the legs in the legs.

The diagnosis of the disease is simple.As mentioned earlier, you can suspect scrotum varicose veins on a normal exam and then a vascular beam ultrasound study should be done to confirm. As a method of treatment, only surgical intervention is used: the doctor simply connects varicose veins, blood circulation is performed according to anastomoses. However, it should be borne in mind that, as in varicose veins, the operation does not guarantee complete healing. In addition, the disease in many cases is recurrent.
Characteristics of varicose veins in women
Pelvic varicose veins.For women, this disease is a risk of fetus encouraging. As mentioned above, varicose veins can occur anywhere in the body, including the pelvic area. During pregnancy, the situation is aggravated because, first, the vessels of the abdominal cavity are stretched as the fetus grows and secondly the uterus increasing in size exerts pressure on them. Due to these processes, the blood circulation of the placenta is disturbed, which can lead to its rejection. In this case, of course, the likelihood of losing a child increases significantly.
Sometimes varicose veins debut during pregnancy.Before conception, a woman could not suspect that she had a tendency to illness. However, during the fetal size period, the female body is subjected to certain changes in the body that can cause some diseases, including varicose veins. Such changes include:
- Changing the hormonal background;
- Increased body weight;
- Anatomical changes.
In addition, the number of births is directly proportional to the risk of obtaining a subsequent pathology. In addition to pelvic varicose veins during pregnancy, other complications may occur:
- Uterine veins rupture during delivery;
- thrombophlebitis;
- dermatitis, trophic ulcers;
- venous deficiency.
Thus, pregnancy is a factor that, unfortunately, can cause varicose veins, as it contributes to the faster development of pathology and requires preventive measures with a certain diagnosis.
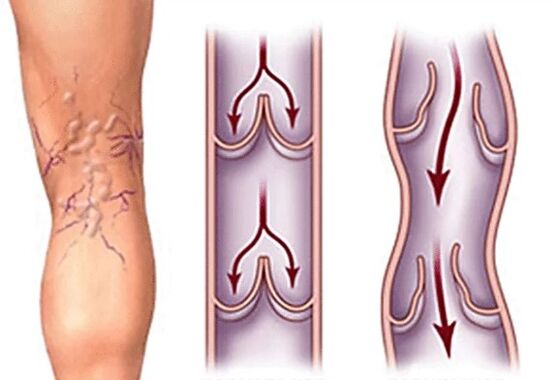
Other consequences of varicose veins
Thrombophlebitis.Often, varicose veins and venous deficiency lead to inflammation of the walls of the blood vessels - flexes, which can be combined with the formation of blood clots - thrombophlebitis. Basically, this disease affects the vessels of the lower extremities as a result of which patients complain of severe pain in the affected areas of the legs. Symptoms of a general inflammatory reaction are observed: high temperature, weakness. If the treatment is not started on time, the process applies to other veins, the patient's condition worsens.
Thromboembolism.In the presence of thrombophlebitis and varicose veins, there is a risk of severe complication - thromboembolism. It occurs due to the separation of the blood clot from the vessel wall, followed by blocking the most important trunks that nourish the heart, light and brain.
Initially, a blood clot can be, for example, in the leg (this is the most common). However, from the lower limb, it is forced to move through the blood flow to various parts of the body. As a result, falling into smaller branches of the vascular system, the blood clot causes a collapse, as a result of which the blood circulation of the site is disturbed by the appearance of ischemia and then necrosis. Clinically, this is manifested by a heart attack, a stroke or pulmonary and fat (pulmonary artery thromboembolism), which usually ends death.
The treatment of patients with this diagnosis should be performed only in intensive care and intensive care units. Measures to assist the patient in this case should be taken immediately - only in this case the patient has a chance of salvation.
Dermatitis.Most of the time, this unpleasant complication occurs on the inner surface of the leg, manifested as various symptoms, including:
- skin tuning;
- epidermal pigmentation;
- itching of the affected area;
- the appearance of bubbles that tend to "open", which leads to stratification of the skin;
- Violation of the sensitivity of the affected area.
Dermatitis does not heal well, it can hardly be treated. The presence of a thrombus implies the occurrence of trophic ulcers - skin death sections. In the future, an infection can join ulcers from which purulent wounds may appear.
TelengioEctasia.This cosmetic defect, which looks like vascular "stars", is a consequence of ruptures of small surface capillaries and an early stage sign of varicose veins.
Hemorrhoids.This is a very common disease - nothing more than varicose veins of the rectum. It is manifested by the emergence of called hemorrhoids called, which are usually able to leave, break and be inflamed. This causes significant concern to patients.
Diagnostic methods
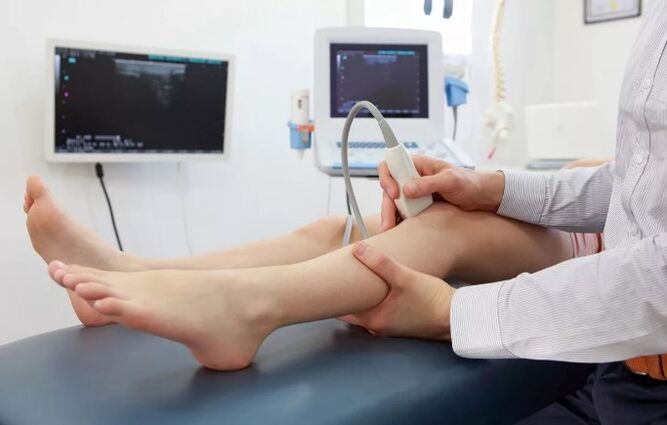
The easiest and most affordable way to detect varicose veins and their complications is the ultrasonic doppler veins of the lower extremities. In the process of this study, blood flow, blood vessels and the condition of their walls as a whole are evaluated. Thus, the above diagnosis helps to detect blood clots. In addition, all patients with varicose veins are needed to pass by Doppler before any surgical intervention in order to exclude the presence of blood clots in order to avoid complications.
In cases where the patient is suspected of venous deficiency or thrombosis, doctors recommend that X-ray contrast phlebography (the method for assessing vein work).
To do this, a special serum - albumin is introduced on the vessel, after which an X root is recorded, on which the impulses from veins will be recorded. So the result is evaluated.
You can complete the exam with computed tomography with the contrast of military trunks. This method is the most accurate, but most expensive. However, this diagnostic method allows not only to identify vascular diseases, but also to evaluate the condition of other body systems and tissues.
Complication treatment
Therapy for the consequences of varicose veins depends on the patient's current state and, directly, the type of complication. Thus, thrombophlebitis requires the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, painkillers. As the inflammatory process disappears, physical therapy is recommended, hirudotherapy (leech treatment) is recommended. An operation can be proposed as an ethyotropic treatment - connection and vein removal.
Trophic ulcers are poorly treated.The surgeon removes the areas of necrosis, prescribes dressings with an anti -space and ointments. Along with these manipulations, antibacterial therapy and blood flow are performed in the vienna.
Vascular stars are eliminated by sclerotherapy, that is, the "collage" of the veins. After the procedure, the use of compression linen for relapse prevention is prescribed.
Other complications, such as hemorrhoids, varicocele and pelvis varicose veins, can only be surgically healed after complete examination and identify the affected vein.
Forecast
An unfavorable prognosis is observed in the case of pulmonary artery thromboembolism, the number of deaths in which it reaches 75%. In addition, thrombophlebitis with trophic skin lesions has a non -enclosed feature, since with this disease occurs persistent changes in blood vessels, and the risk of infection is also increased, which leads to various complications. The consequences of the disease can usually lead the patient to disability.
The indications for the supply of a patient for disability are:
- the presence of thrombosis and transferred thromboembolism;
- recurring erysipelas;
- Post -Fluboflebetic Syndrome;
- Ineffective surgical treatment.
Most of the time, disability is given to patients with the last stage of varicose veins with persistent impaired performance.